Two important processes should be distinguished in relation to the supply of electric power – ensuring physical flows of electricity (provided by the power grid) and electricity trading (wholesale and retail market) in the form of commercial transactions. To ensure continued supply of electricity to users, it is essential to ensure the continuity and high quality of these processes. For more about supplying electricity, see the section Transmission network. 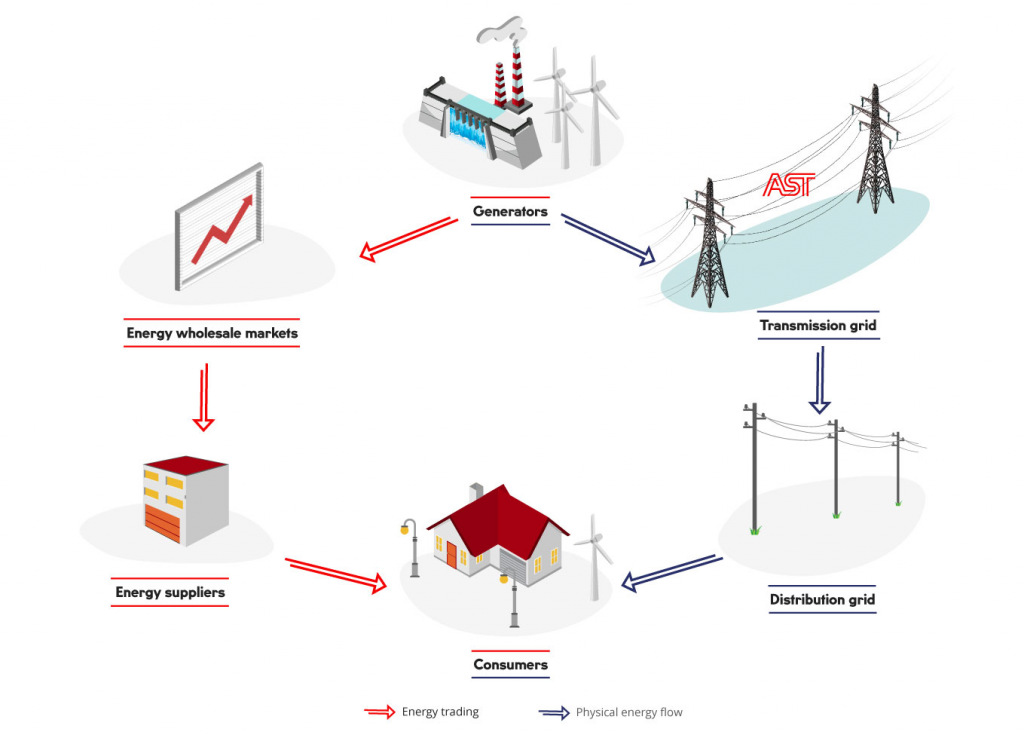
The basic principle of an integrated electricity market is that the electricity from the cheapest area flows to areas with a higher price, while respecting cross-border connections limitations between countries and their price areas. Differences in electricity prices in different bidding areas can be explained by differences in demand and supply of electricity. The Latvian electricity market at the wholesale level is directly integrated with the Baltic States and the Nordic countries, whereas the retail market is organized at the national level.
The legal framework for the electricity market in Latvia is the Electricity Market Law that stipulates that the transmission system operator, with its functions, should facilitate the operation of the internal electricity market and cross-border trade, including the support of electricity exchanges development.
Latvia is an integral part of the European Union's internal electricity market, which operates in accordance with the principles of EU policy and norms of law acts. The integration of the Latvian electricity market into the EU market began in 2009 when the Baltic Energy Market Interconnection Plan (BEMIP) was approved.
In line with the principles of the single integrated electricity market adopted by the EU, there are several interconnected stages in the electricity market functioning that are subordinate to the time moment - from the long-term (forward markets) to the real-time (balancing) market and the operation of the energy system.
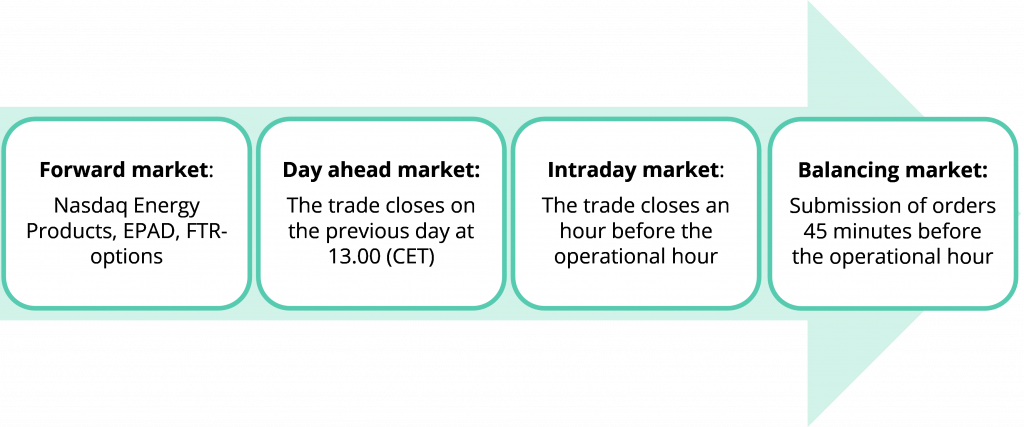
In center of this market model is the day-ahead and intraday electricity markets operation
Electricity market participants (producers, traders, aggregators and electricity end users) operate in the electricity market in accordance with the principle of voluntary participation and their commercial transactions cover the supply of electricity from the producer to the user. Initially. these transactions take place in the wholesale electricity market and afterwards in the electricity retail market.
Retail market
In the retail market, the transactions by the market participants include sales of electricity between the electricity user and trader according to a mutual electricity trading agreement. Transactions carried out in the retail market provide electricity both to legal entities and households. By concluding an agreement, the electricity user purchases electricity from the trader whose proposed price and offered services are the most favourable.
Operation of wholesale and electricity exchange
Wholesale transactions are carried out between electricity traders and producers. All trading transactions take place mainly on the electricity exchange or, in rare cases, in the form of fixed deliveries.
Fixed supply means the oportunity to purchase electricity at a fixed price from the respective trader or producer.
The proportion of transactions performed in the form of fixed deliveries is significantly lower compared to transactions performed on the electricity exchange.
Within a single trading area, transactions involving the physical transmission of electricity may be carried out by market participants both on the electricity exchange and by mutual agreement.
Electricity transactions on the exchange are based on the interaction of user/buyer demand and producer/seller supply. The demand amount is determined by the users'/buyers’ needs and the supply - by the electricity producers' possibilities, as a result of which the price of electricity is determined. Electricity traders and producers carry out transactions on the electricity exchange.
Transactions that exceed the limits of a particular trading area and encompasses physical transmission of electricity must be conducted within the electricity exchange only.
The electricity exchange in Latvia started operating in 2013. The exchange ensures the electricity markets integration with other European Union Member States electricity markets, with which the Latvian electricity system has interconnections.
Currently, one nominated electricity market operator (electricity exchange), which is Nord Pool AS, operates in Latvia. Nord Pool performs the operation of the electricity exchange, in framework of which the day-ahead and intraday electricity markets are working. Nord Pool homepage contains updated market information. For more details, see https://www.nordpoolgroup.com/
On the exchange, the electricity trading transactions are organised in two processes:
- day ahead market;
- intraday market.
The day ahead electricity market allows the market participant to submit their price proposals for transactions taking place the following day. Meanwhile, in the intraday market participant can submit their requests and proposals for transactions on the current day, not later than one hour before the operation hour.
The day-ahead electricity price is determined on the previous day, combining all the requests and offers together and setting a single price for each hour and each trading zone.
The intraday electricity price is determined by continuous trading, which combines certain offers and requests, and the price is determined on the basis that the first request receives the best price from the traders’ offers.
Operation of both markets ensures high liquidity of the Latvian electricity market, as well as more efficient use of capacity and provides market participants with reliable and transparent electricity prices.
Electricity trading risk hedging instruments (Forward Market)
Taking into account the volatility of electricity prices, electricity market participants can limit the volatile price risk by using financial instruments.
In Latvia, two electricity trading risk hedging instruments (Forward Market) are available:
- NASDAQ Energy Products – hedging oportunities for price difference between trading areas (EPAD);
- The Financial Transmission Rights-option on the Estonian-Latvian border provided by AS “Augstsprieguma tīkls” and Elering, for more information see PTR-Limited auctions
Balancing market
All transactions (both wholesale and retail) are not only related to the commercial interests of the market participants, but also play a significant role in ensuring system balance. The trading transaction plans are sent to the transmission system operator on a daily basis to ensure compliance with the technical capabilities. In addition, the transmission system operator is responsible for ensuring the balance of the power system, regardless of the accuracy of the trading plans. To avoid balance deviation, the transmission system operator purchases balancing services in the balancing market. Read more about the system balancing and the common Baltic balancing market here.
